Nitrosamine Impurities & customized Reference Standards
Home » Chemical Services » Nitrosamine Impurities Reference Standards
We enable holistic risk management of nitrosamine impurities and advise pharmaceutical companies on how to adjust their processes
- Your product ingredients or manufacturing process might be vulnerable to nitrosamine formation?
- Confirmatory testing is the last chance to prevent a potential market recall or suspension of your product?
- Reference standards for reactivity assessment and risk management are commercially not available?
- Need of a one-stop-shop covering chemical and analytical support as well as regulatory and strategic advice?
Due to our outstanding expertise in synthetic chemistry, our equipment for analytical chemistry and handling of highly potent and hazardous substances (in a glove box), we were able to build a proven track record in supporting pharmaceutical companies along their process of risk assessment and management of nitrosamine impurities. Nitrosamines might be identifed as impurities in ingredients, as degradation products or throughout the whole manufacturing process. While others may only provide reference standards (e. g. catalogue provider) or analytical services (testing laboratories), our customers benefit from one-stop-shop services covering:
- Customized reference standards for biological testing of nitrosamine impurities
- Quality control and structure confirmation of synthesized nitrosamine compounds
- Determination of detection limits (LODs) of synthesised nitroso degradants
- Root cause analysis to trace back all starting materials and excipients besides the API
- Solubility studies to support Ames Tests & purge factor analysis to understand strategy options
- Stability studies to support Ames Tests, evaluation of the shelf life & introduced nitrosamines
- Further strategic consultancy on chemical and regulatory issues to adjust the processs
Nitrosamine impurities bear the risk of drug product recalls
In 2018, some sartan medicinal products were reported to be contaminated with nitrosamine compounds, which are potent mutagenic carcinogens. In response to that discovery, drug formulations containing different sartans as active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs) were recalled by various pharmaceutical firms. Major regulators withdrew a series of medicines containing sartans, ranitidine, and metformin.
Official guidances by FDA (Control of Nitrosamine Impurities in Human Drugs | FDA-2020-D-1530 updated in February 2021) and by EMA (Nitrosamine impurities in human medicinal products | EMEA/H/A-5(3)/1490, June 2020) advise manufacturers of APIs and drug products to detect and prevent objectionable levels of nitrosamine impurities in pharmaceutical products. This strategy includes risk assessment (step 1) of all drugs containing chemically synthesized APIs, confirmatory testing if risks are identified (step 2) and reporting of appropriate actions to reduce/prevent the presence of nitrosamine impurities (step 3). While risk assessments should have been completed in March 2021, the FDA expects confirmatory testing and reporting to be completed in October 2023, and the EMA even expects completion by September 2022.
This guidance applies to all chemically synthesized drugs on the market and those under current review. These groundbreaking regulations are expected to evolve rapidly to limit human exposure to nitrosamine impurities, since a lot of ingredients, degradation products and manufacturing processes are vulnerable to the formation of N‑Nitroso compounds.
Looking for nitrosamine impurities reference standards?
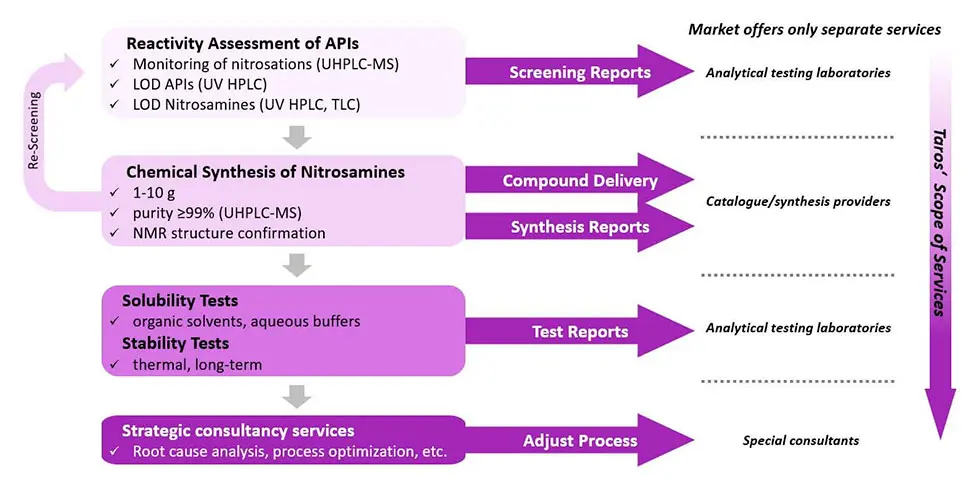
Our workflow for confirmatory testing of nitrosamine impurities
First, we set up a screening panel to assess of reactivity of target compounds such as APIs towards nitrosation at different concentrations of nitrosating agent, reaction times and reaction temperatures. Screening reactions are done in parallel under different conditions and are monitored by UHPLC-MS. Based on the first screening results, the target compounds are classified and selected for further isolation. In cases where nitrosamine formation is suspected but not reliably detected, re-screening with the synthesized reference standards will be followed up.
The limits of detection (LODs) of the target compounds are determined in UHPLC based on UV absorption. Identified nitrosamines, which can be potentially formed from APIs with secondary and/or tertiary amines, are synthesized in quantities depending on complexity of the structure. Considering relevant pharmacopeia, all impurities with the same structural prerequisites and the potential to form nitrosamines are synthesized as well. Nitroso degradants are isolated with a purity of ≥99% in UHPLC and structures are further confirmed by NMR. LODs of synthesized nitroso degradants are finally determined using relevant analytic methods like UHPLC-MS.
At the end, we conduct solubility tests (organic solvents, aqueous buffers) to support a purge factor analysis, which is crucial to understand nitrosamine-related risk and control strategy options. Stability tests (thermal, long-term) are conducted to assess the shelf life of the investigated compound or nitrosamines that could have been introduced within the route of the synthetic process. Especially the nature and stability of the diazonium/carbenium ion is a relevant factor to determine its carcinogenic potential. All information will result in a final test report, which also provides recommendations for a follow-up strategy to conclude the process of risk assessment and confirmatory testing of nitrosamine impurities.
Frequently asked questions on nitrosamine impurities
In contrast to pure analytic testing laboratories or chemical synthesis & catalog providers, Taros provides one-stop shop services from supporting risk assessment and confirmatory testing of nitrosamine impurities to further strategic consultancy on chemical and regulatory issues to adjust the clients’ processes according to regulatory guidelines. As a successful contract research organization (CRO), we have been working on thousands of discovery chemistry projects including reference standards and detection of impurities for pharmaceutical, biotech and chemical companies since 1999. We have experienced chemists as well as the necessary equipment and infrastructure to support companies along their process of reactivity assesment and risk management of nitrosamine impurities.
We employ a customer-centric approach as well as a flexible business model to dedicate our services to sophisticated chemistry challenges within very narrow timelines. Every customer will have a dedicated project manager in the course of a project to ensure effective and transparent communication on the progress of the project as well as close scientific exchange to anticipate any upcoming issues. Since holistic risk assessment and confirmatory testing of nitrosamines is a huge undertaking, companies rely on a capable partner like Taros.
Contact our scientific business development team, they will be happy to advice you on your specific requirements – Get in touch!
Regulators like the EMA and FDA evaluate APIs and finished drug products for formation and cross-contamination of nitrosamines. Large scale product recalls and suspensions might be the consequences.
Following the detection and quantitative determination of N-nitrosodimethylamine (NDMA) in Ranitidine, EMA requires preventive reactions like a risk assessment on the formation an presence of N-nitrosamine in drug products. Marketing Authorization Holders (MAHs) should review all medicines to identify and mitigate the risk of the presence of nitrosamine impurities. If nitrosamines are positively tested, the MAH must inform the authority (irrespectively of the amount). Focus is on drug products and ingredients like APIs as well as excipients which contribute to the risk profile of the drug product.
Examples of nitrosamines in drug Products:
- Valsartan: since June 2018, recalls worldwide and CEP suspensions
- Ibesartan, Losartan: since July 2018. several recalls and CEP suspension
- Pioglitazone HCL: since April 2019, NDMA at low levels, but no market actions so far in the EU
- Ranitidine: since September 2019, several recalls (US, EU) and suspension of market approvals (EU, US)
- Metformin: since December 2019, market actions and recalls (extend-release dosage forms)
While risk assessments should have been completed in March 2021, the FDA expects confirmatory testing and reporting to be completed in October 2023, and the EMA even expects completion by September 2022. This guidance applies to all chemically synthesized drugs on the market and those under current review.
Contact our scientific business development team, they will be happy to advice you on your specific requirements – Get in touch!
Besides ingredients of a drug product like the APIs and excipients, nitrosamines can be formed in many products of different industries such as:
- agricultural chemicals
- tobacco
- detergents
- solvents
- plastics
- cosmetics
- and many more
Contact our scientific business development team, they will be happy to advice you on your specific requirements – Get in touch!
N-Nitrosamines can be formed from amines and nitrosating agents (generally oxidized nitrogen containing compounds, NOx) under certain reaction conditions. These NOx species have different reactivities and can react with amines differently depending on, for example, the pH of reaction media and the nature of the solvent. At low pH, the more powerful nitrosating reagents are present, but the amine is more protonated, and thus, less reactive. Therefore, effective nitrosating conditions depend both on the pH and the basicity of the amine. Nitrous acid forms salts with basic amines which, when heated, can further react to afford N-nitrosamines.
There are different pathways for N‑Nitroso compound formation:
- N-N bond formation
- N-O cleavage
- N-O formation
- Miscellaneous routes including various nitrosating reagents like peroxynitrite, Fremy’s salt, etc.
Contact our scientific business development teams, they will be happy to advice you on your specific requirements – Get in touch!
General root causes might be:
- General conditions that lead to nitrosamine formation.
- Formation is possible in the presence of secondary, tertiary, or quaternary amines and nitrite salts under acidic reaction conditions.
- Sources of secondary, tertiary, and quaternary amines that can form nitrosamines.
Amines may be present in a manufacturing process for a variety of reasons. The API (or API degradants), intermediates, or starting materials may contain secondary or tertiary amine functional groups. - Contamination in vendor-sourced raw materials.
- Cross-contaminations due to different processes run on the same line and due to operator-related errors such as inadequate phase separations.
- Recovered solvents, catalysts, and reagents as sources of contamination.
Recovered materials such as solvents, reagents, and catalysts may pose a risk of nitrosamine impurities due to the presence of residual amines. - Quenching process as a source of nitrosamine contamination.
There is a risk of nitrosamine formation when a quenching step is performed directly in the main reaction mixture (i.e., when nitrous acid is added to the reaction mixture to decompose residual azide). - Lack of process optimization and control.
In case reaction conditions such as temperature, pH, or the sequence of adding reagents, intermediates, or solvents are inappropriate or poorly controlled).
Contact our scientific business development team, they will be happy to advice you on your specific requirements – Get in touch!
Up to now, regulators have only evaluated APIs and finished drug products for formation and cross contamination of nitrosamines. There are no regulatory or testing requirements for the excipient manufacturer to assess the formation of nitrosamines in excipients.
However, as excipients are constitutents of the drug product, they are a part of the drug product risk evaluation as well. The FDA raises concerns about the presence of nitrites as nitrosating agents. Nitrite impurities may also vary across excipient lots and supplier. The potential presence of nitrites may pose a risk for nitrosamine formation at various stages:
- During the drug product manufacturing process
- During shelf-life storage period
- If the nitrosatable structure is present with another component /impurity of the drug product
Even the use of certain packaging materials may be a source for nitrosamines (Nitrosamine contamination has been observed by one Marketing Authorization Holder (MAH) in a finished product stored in blister. The MAH has hypothesized that the lidding foil containing nitrocellulose printing primer may react with amines in printing ink to generate nitrosamines, which would be transferred to the product under certain packaging process conditions).
Contact our scientific business development team, they will be happy to advice you on your specific requirements – Get in touch!
The FDA has identified seven nitrosamine impurities which may be present in chemically synthesized APIs and drug products. The first five have already been detected in marketed drugs. While the last two have not been detected so far, experts assume their presence as highly probable. The FDA has suggested interim acceptable limits for six of these nitrosamine impurities (see table below).
| Nitrosamine | Acceptable Intake Limits (ng/day) |
| N-nitrosodimethylamine (NDMA) | 96 |
| N-nitrosodiethylamine (NDEA) | 26.5 |
| N-nitroso-N-methyl-4-aminobutanoic acid (NMBA) | 96 |
| N-nitrosomethylphenylamine (NMPA) | 26.5 |
| N-nitrosoisopropylethyl amine (NIPEA) | 26.5 |
| N-nitrosodiisopropylamine (NDIPA) | 26.5 |
| N-nitrosodibutylamine (NDBA) | unspecified |
The European medicines Agency (EMA) has established temporary interim limits for NDMA, NDEA, NMBA, NDIPA, and NEIPA for sartan products based on the maximum daily dose.
Contact our scientific business development team, they will be happy to advice you on your specific requirements – Get in touch!
Drug Discovery

Material Science
We create performance chemicals to enhance new materials, plastics, coatings, dyes & inks, cosmetics, flavors and many more research and industrial applications…